Key role of plant nutrition for soil health
Soil is the foundation of food production. Life on earth depends on it.
Soil health is vital for ensuring the resilience of European ecosystems in the face of our changing climate, and for providing the EU with sufficient, safe and nutritious food. Soil health is farmer´s major asset for sustained and sustainable food production.
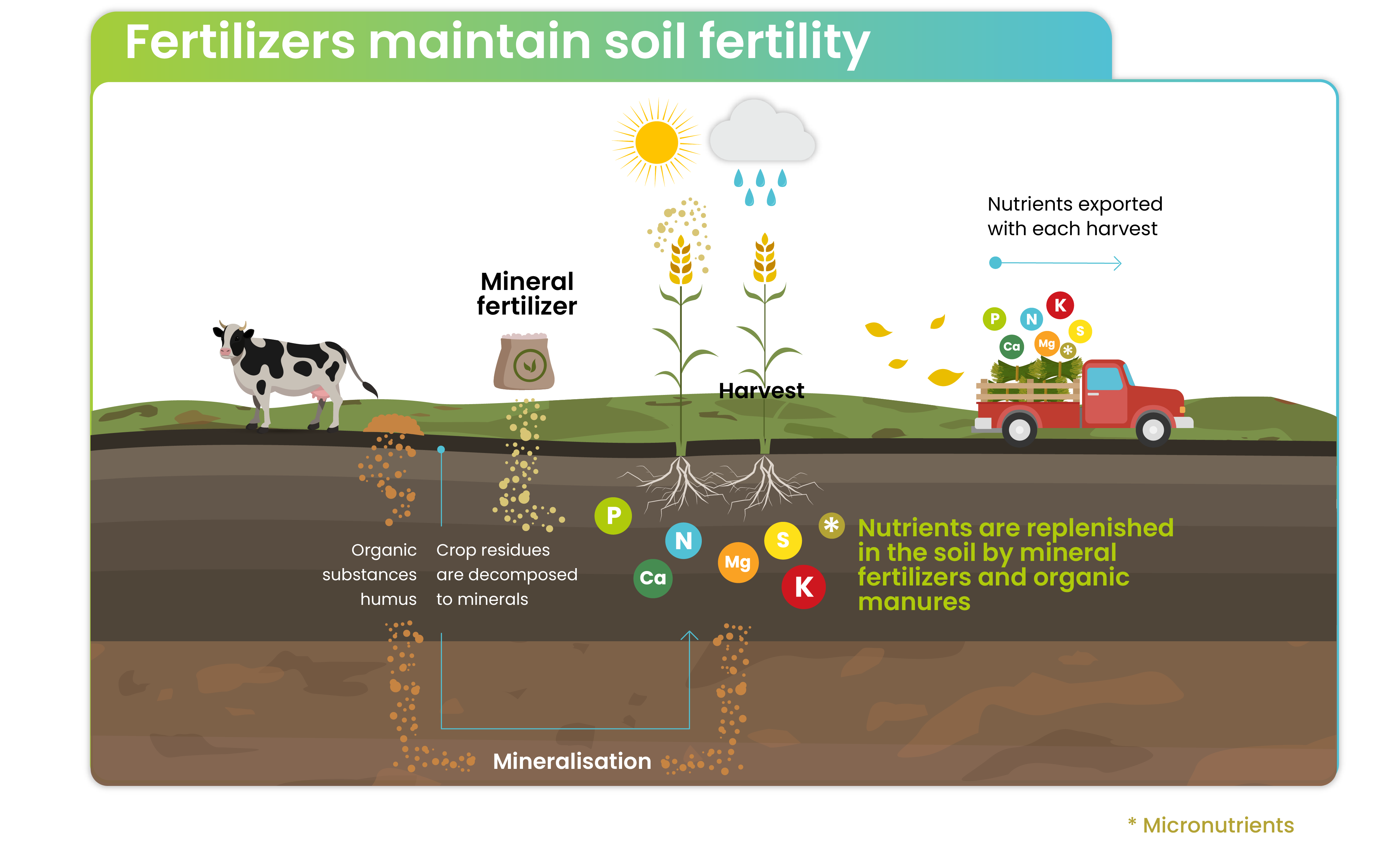
The fertilizer industry is inextricably tied to soil health as its role is to provide essential nutrients that are key for healthy and resilient plant growth, preventing nutrient depletion and maintaining fertility over time.
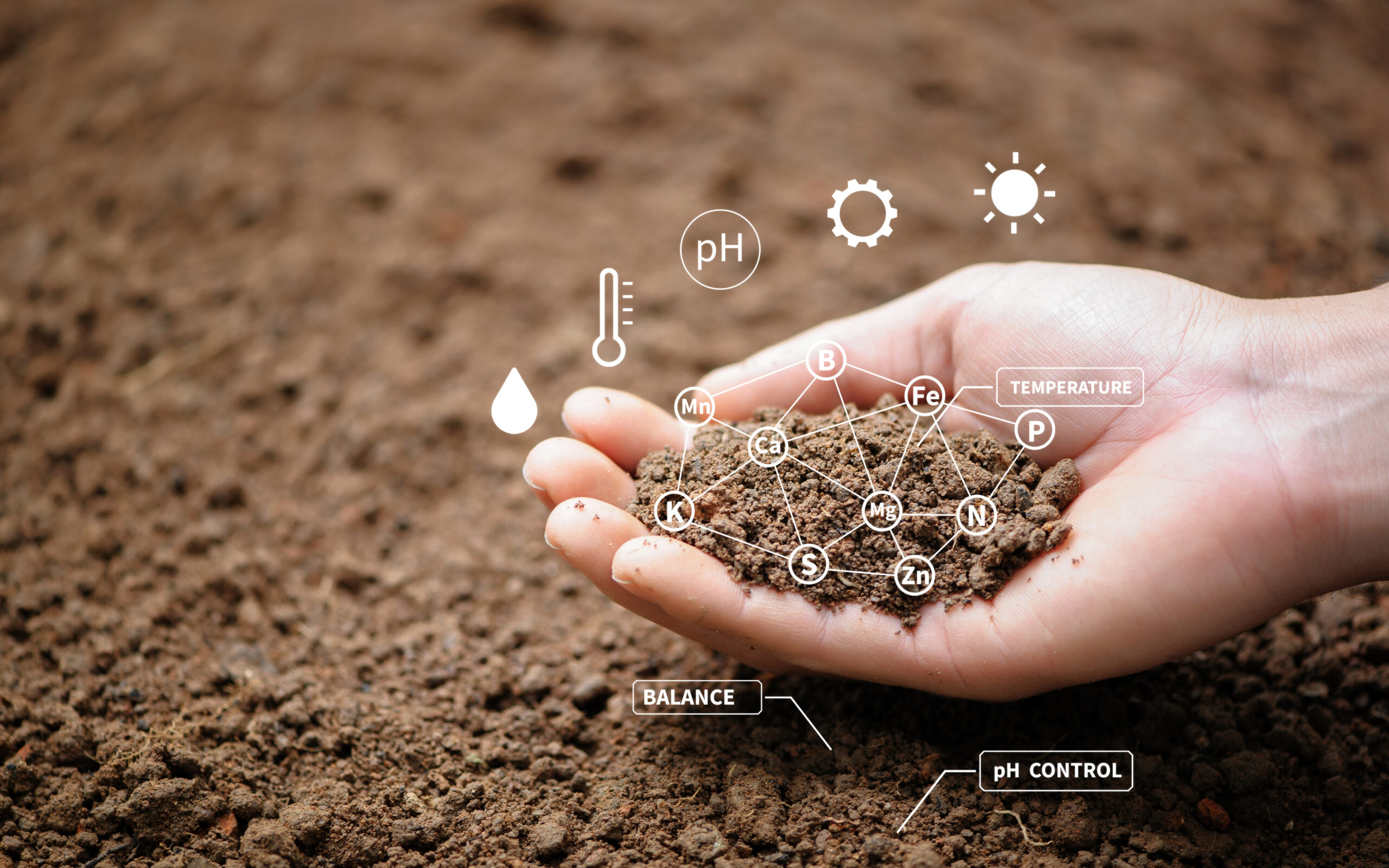
Soil is a complex mix of minerals, organic matter, gases, liquids, and organisms. Its health involves diverse factors like nutrient levels, pH, structure, and ability to support plants and ecosystems. Assessing soil health needs a comprehensive approach using various indicators to get a full picture. This is vital for informed decisions in farming and environmental management.

On July 5th the European Commission published its proposal for a Directive on Soil Monitoring and Resilience (Soil Monitoring Law) providing a starting point for the development of an EU Monitoring Framework for European Soils.
What should this Directive consider to ensure healthy soils?

Consider both nutrient excess and deficiency as parameters for agricultural soil health
Maintaining adequate nutrient levels in the soil is crucial to support robust crop yields. Balanced plant nutrition ensures plants’ access to an adequate supply of each nutrient at every growth state, regardless of whether their origin is mineral or biological. Maintaining soil fertility is critical for crop production, and for the capacity of the soil to maintain the growth of plants and, hence, for the soil health itself. Degradation in agricultural soils occurs when the soil loses its ability to supply needed nutrients for crop growth and food production.

Phosphorus Management: Rethinking Limits
Defining one single limit for all soils does not represent the right approach. Considering diverse soil types and their individual needs is crucial for yields and agricultural productivity.
The phosphorus monitoring should be designed in a way that addresses the real environmental concerns (P losses into the environment) and preserve farmers’ ability to address the specific phosphorus requirements of their crops on a field, while maintaining soil fertility and soil health. Soil health is farmer´s major asset for sustained and sustainable food production.
.

Ensure a level playing field across EU Member States
The development of a legislation largely at the Member State level is a step in the right direction. However, further support and technical assistance is needed to avoid the risk of fragmentation and potential uneven playing field between different Member State.

Encourage the development of science-based thresholds at Member States level
Nutrient thresholds in agricultural soils shouldn’t restrict crops with high nutrient needs. Strict limits, like the 30-50 mg/kg extractable phosphorus, might discourage planting such crops, affecting productivity and food security. Granting flexibility in the implementation of soil management strategies in agricultural soils would enable farmers to adapt practices tailored to their specific soil types and regional conditions.
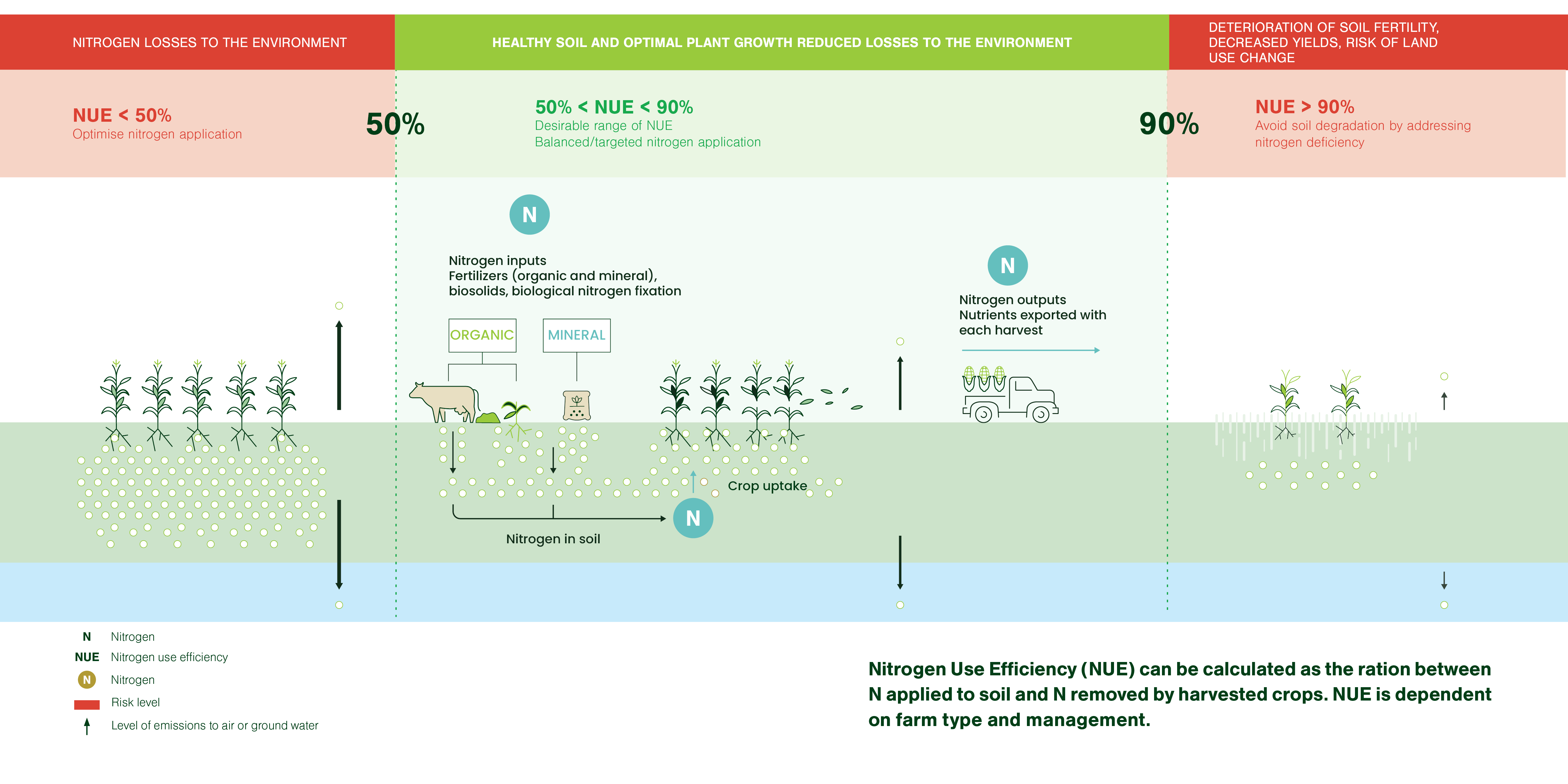
Introduce Nutrient Use Efficiency among the Sustainable Soil Management principles
The concept of Nutrient Use Efficiency (NUE) represents the ability to provide for the nutrient needs of plants, while avoiding losses to the environment. The result is an agricultural system that is capable of achieving European food security through high yields with high quality crops, while also ensuring soil health, biodiversity, and long-term agricultural fertility
The Nitrogen Use Efficiency Indicator

Replace the One-Out-All-Out criterion with a Soil health index
Relying on a single criterion overlooks soil’s complexity. A soil health index considering various indicators such as physical, chemical, and biological properties, would offer a more context-specific and comprehensive approach reflecting the overall health and quality of the soil

Ensure Regulatory Consistency
Industrial soils are already subject to regulation under various pieces of legislation. It’s essential to optimize compliance efforts for industries while ensuring effective environmental protection and risk management for industrial soil sites.